Quick question: What do you think will power the 4th industrial revolution?
If you answered off the top of your mind, these probably were on top of your list: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Nanotechnology, or Biotechnology.
And you’re right. But while the focus seems to be on these more popular concepts, there is one bubbling field that is almost going unnoticed; 3D printing.
What is 3D Printing or Additive Manufacturing?
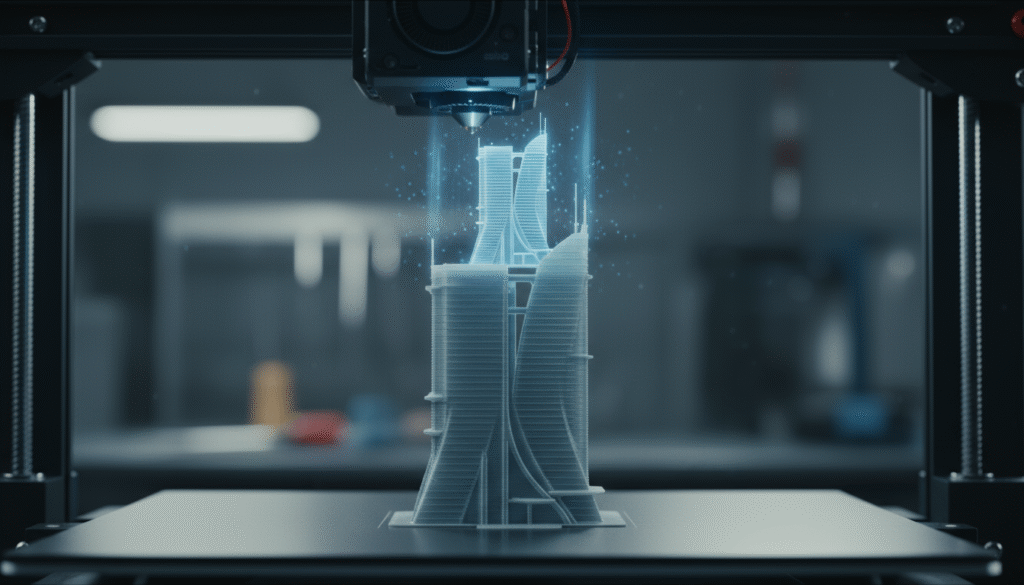
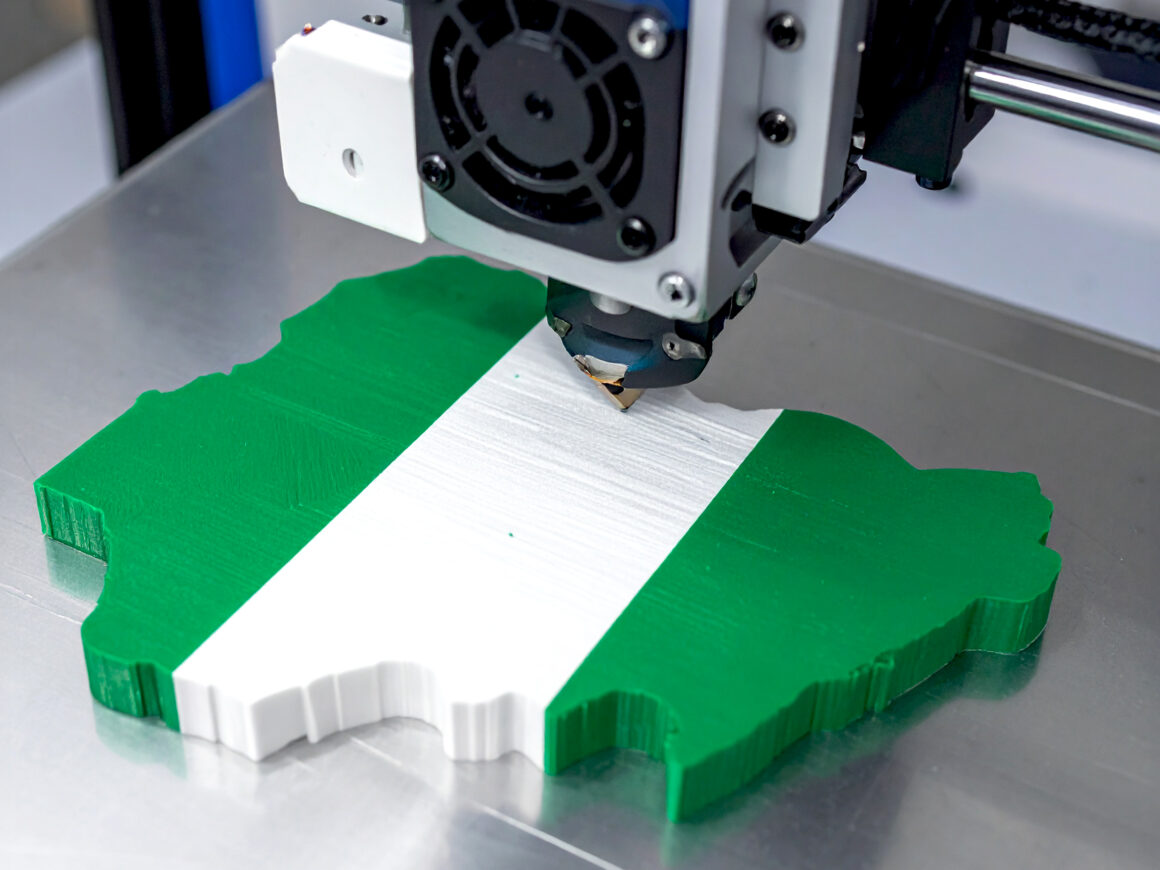
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is the process of building three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital design.
What this means is that people can now think of an object they would like to create, sketch and illustrate it, decide on the best materials for it, and then go ahead to manufacture it from scratch, layer by layer.
In Nigeria, where small businesses and startups are rapidly growing, additive manufacturing provides an affordable pathway to produce high-quality goods locally without the heavy overheads of traditional factories.
Common Methods of 3D Printing
3D printing is not a single process but rather a family of manufacturing methods. The three most recognized are:
Additive Manufacturing
The most popular form, where products are built layer by layer from raw material. This is what most people think of when they hear “3D printing.”
Subtractive Manufacturing
This involves cutting away material from a larger block to form a product, common in traditional machining. While precise, it generates more waste compared to additive methods.
Formative Manufacturing
Here, raw material is shaped into form using molds, stamping, or casting. While efficient for mass production, it lacks the customization and flexibility of additive manufacturing.
3D printing or additive manufacturing reduces production waste while giving room for customization. It’s no surprise that it’s fast becoming the go-to approach for creating custom objects in Nigeria.
3D Printing in Nigeria: What Difference Will It Make?
The global 3D printing market was estimated at $19.33 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow from $23.41 billion in 2025 to $101.74 billion by 2032.
And Africa’s entire footprint? Only about $2.83 billion in 2024, projected to hit $7.32 billion by 2031.
Nigeria is gradually fighting for a slice of the pie, and although the Nigerian market share is a rather negligible chunk now, it still counts for something.
This new era of innovation is particularly exciting for Nigeria because traditional manufacturing methods, which require massive capital investment and lengthy production cycles, are no longer the holy grail since 3D printing now empowers businesses, schools, and innovators to create products on demand, locally and affordably.
For Nigeria, this technology offers solutions to long-standing issues such as reliance on imports, high unemployment, and limited access to affordable products in healthcare, housing, and education.
Benefits of 3D Printing
Beyond making it possible to create custom objects, 3D printing offers a number of benefits across different sectors.
Reduced Production Costs
Unlike mass production, which requires expensive molds and tooling, 3D printing minimizes upfront costs. This way, Nigerian entrepreneurs can produce items affordably, especially in low-volume manufacturing.
Faster Turnaround and Rapid Prototyping
Businesses can design, prototype, and test products in days instead of months. This speed accelerates innovation in Nigeria’s startup ecosystem, enabling quicker time-to-market.
Customization and Personalization
From prosthetic limbs tailored to individual patients to personalized fashion accessories, 3D printing makes customization affordable and accessible.
Sustainability and Waste Reduction
Because it uses only the material needed for each design, 3D printing reduces waste, a vital step toward sustainable industrialization in Nigeria.
How 3D Printing Synergizes with AI & Emerging Tech

While 3D printing alone is powerful, its future impact really multiplies when it’s paired with artificial intelligence, wearables, and other cutting-edge technologies. These connections are already showing up globally, and they hint at what Nigeria’s innovation scene could achieve soon.
Real-World Signals Case Studies
- A recent wearable called Friend is essentially a pendant that listens, responds, and converses using AI (specifically a chatbot backend). While it isn’t yet clear if its casing is being 3D printed, the concept shows how hardware design (including enclosures and ergonomic components) will demand fast, customizable manufacturing methods; that’s where 3D printing shines.
- Researchers at Arizona State University are developing AI tools to improve reliability in metal 3D printing (for example, reducing defects and predicting material behavior during the build). These improvements make additive manufacturing more scalable and precise.
- In Japan, companies are integrating AI into their 3D printing pipelines to speed up material discovery and optimize print precision, reducing costs and enabling designs that meet stricter performance or sustainability criteria.
Championing the Introduction of 3D Printing into the Nigerian Market
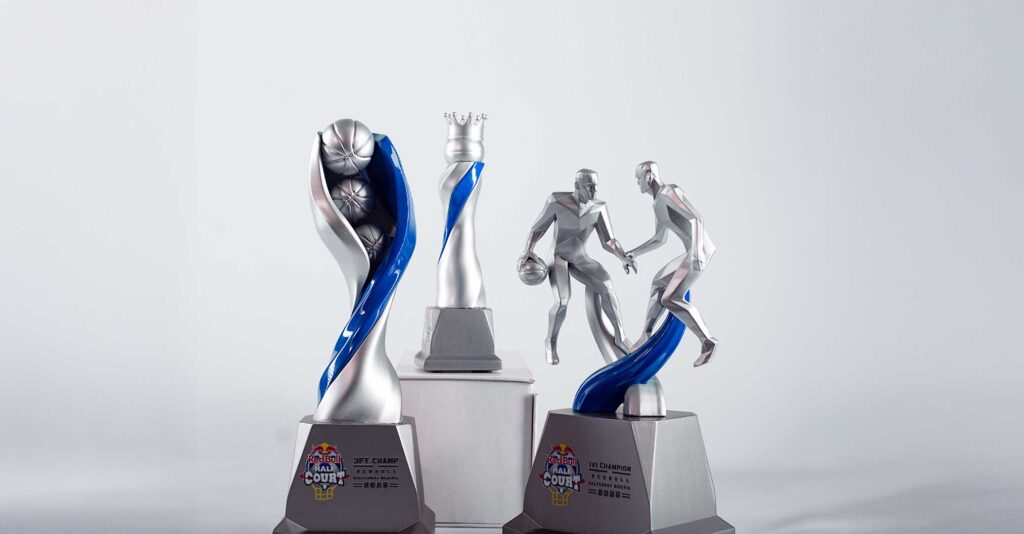

Although 3D printing is still relatively new in Nigeria, few companies have ventured into exploring the potential that the 3D manufacturing industry offers.
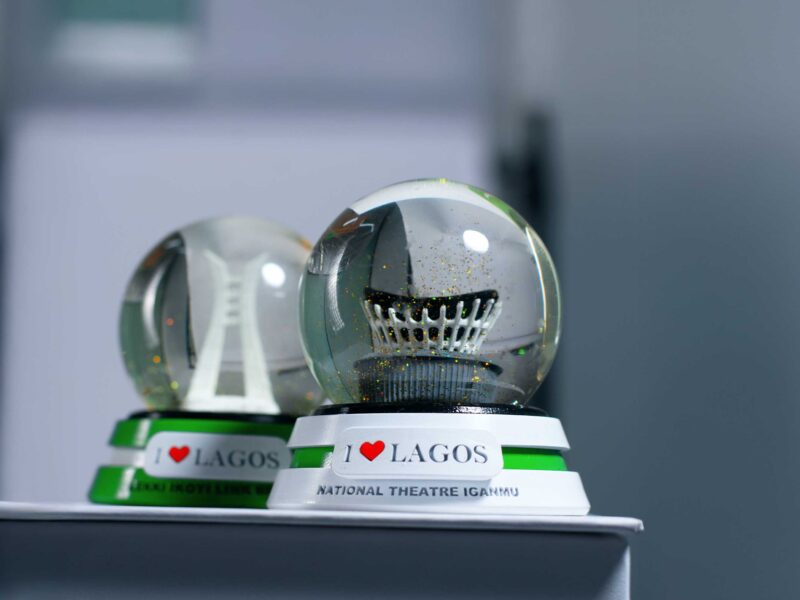
Meta4 is one of the companies using 3D printing to create functional objects for brands and individuals across various industries. By offering easy access to high-quality 3D printing services, Meta4 is bridging the gap between Nigerian entrepreneurs and modern manufacturing tools.
From anatomical and educational models to architectural models and corporate gifts, we have built a solid portfolio of exquisitely designed 3D-objects, crafted from scratch in Nigeria. Check our product catalogue here
Conclusion
The arrival of 3D printing in Nigeria is a transformative force capable of reshaping industries, empowering entrepreneurs, and improving lives.
From healthcare and housing to fashion and education, the benefits are far-reaching. By embracing additive manufacturing, Nigeria has an opportunity to reduce dependency on imports, build a resilient economy, and foster a new era of local innovation.
With pioneers like Meta4 leading the charge, the future of 3D printing technology in Nigeria is inevitable.






